- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-12 Origin: Site








A motor starter is critical for safely starting and stopping motors, while also protecting them from damage. How exactly does it work? Understanding its components, like the Motor starter, Multi-function motor starter, and Motor control and protection switch, is key to ensuring reliable motor performance. In this article, we'll explore how these systems control power flow, prevent damage, and optimize motor operation.
A contactor is an electrically operated switch that plays a central role in motor starters. It controls the power flow to the motor by either closing or opening the circuit, allowing current to flow through the motor when it’s time to start or stopping it when needed. The contactor is energized by a control circuit, and its main purpose is to make or break the electrical connection between the motor and power supply.
The overload relay is crucial for protecting the motor from excessive current and heat. If the motor draws too much current—whether due to mechanical overload or a fault—the overload relay will disconnect the power to the motor, preventing further damage. This component ensures that motors are not exposed to hazardous conditions that could lead to overheating or burnout.
Motor control and protection switches are designed to offer additional safeguards for the motor and the entire system. These switches help ensure that the motor starts and operates under safe conditions, offering protection against issues like overvoltage, under-voltage, and short circuits. Integrated with the motor starter, they provide both manual and automatic control, improving the reliability and safety of motor operations.
Motor starters work by controlling the flow of electrical power to a motor in a way that prevents damage during startup. The primary function of a motor starter is to gradually apply power to the motor, managing the initial surge of current (inrush current) that can be damaging. The starter is activated by pressing the start button, which sends a signal to the control circuit to energize the contactor, closing the circuit and allowing current to flow to the motor.
A motor starter consists of two key circuits: the power circuit and the control circuit. The power circuit connects the motor to the electrical supply, transmitting current to the motor. The control circuit, on the other hand, is responsible for operating the contactor, which opens or closes the power circuit. The control circuit uses a low-voltage signal to energize the contactor coil, which in turn pulls the contacts together, allowing current to flow to the motor.
Motor starters also enable the motor to be safely stopped. Pressing the stop button de-energizes the contactor, breaking the power circuit and halting the motor. In addition, the overload relay will disconnect the motor from the power supply if the current exceeds safe levels, ensuring protection during both startup and shutdown.
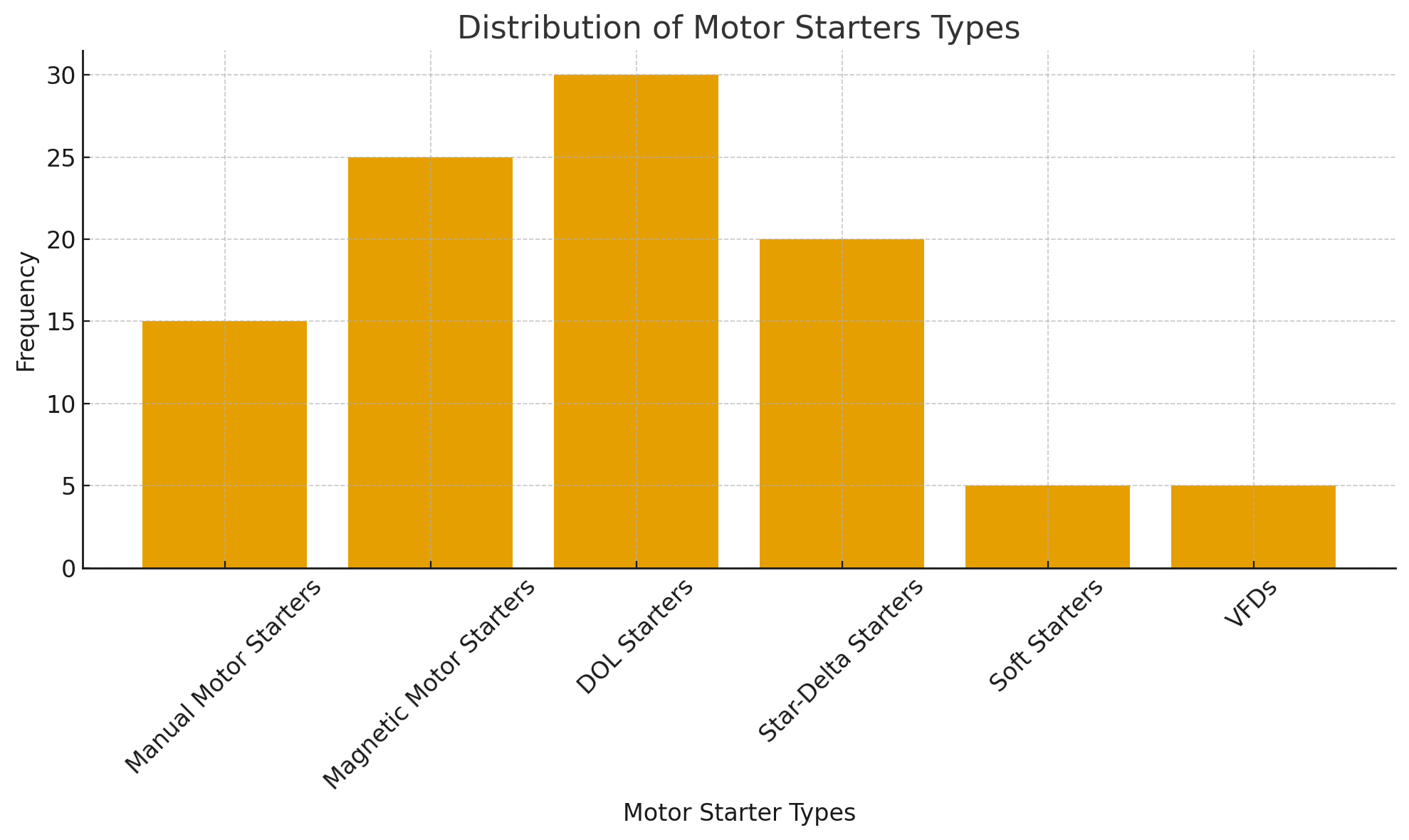
Manual motor starters are the simplest form of starters, typically using a button or lever to start and stop the motor. These starters are best suited for small motors or systems where automatic control isn’t necessary. While inexpensive, manual starters lack certain safety features like protection against power failure, making them less ideal for larger or critical systems.
Magnetic motor starters use an electromagnetic coil to control the operation of the motor. When the coil is energized, the contactor closes and allows power to flow to the motor. These starters are ideal for applications where remote control and automated operation are necessary, as they offer protection from low voltage, overcurrent, and short circuits.
The DOL starter is the most straightforward and cost-effective motor starter. It directly connects the motor to the power supply, applying full voltage to the motor. While this starter is simple to use, it’s only suitable for small motors due to the high inrush current it causes during startup. DOL starters are best for applications where the motor's startup current won’t cause damage or voltage dips.
Star-Delta starters are designed to reduce the inrush current during motor startup. Initially, the motor is connected in a star (Y) configuration, which reduces the voltage across the windings, limiting the starting current. Once the motor reaches a certain speed, the starter switches to a delta (Δ) configuration for normal operation. This type of starter is ideal for larger motors, providing a smoother and more efficient startup.
Soft starters are electronic devices that gradually increase the motor's voltage during startup, reducing the mechanical and electrical stress on the motor. These starters are commonly used in systems requiring smooth acceleration, such as HVAC systems, conveyors, and fans. Soft starters extend the lifespan of the motor by preventing sudden power surges and reducing wear and tear.
VFDs provide precise control over the motor’s speed and torque by adjusting the frequency and voltage of the power supply. VFDs are particularly beneficial in applications that require variable speed, such as conveyors, fans, and pumps. In addition to offering energy savings and better process control, VFDs also provide a soft start function, reducing the impact of inrush currents.
Overload protection is crucial for preventing the motor from overheating due to excessive current. Motor starters with overload protection use a relay to detect when the motor draws more current than it can safely handle. If an overload is detected, the relay disconnects the motor from the power supply, preventing damage and extending the motor’s lifespan.
Motor starters are equipped with short-circuit protection, often in the form of circuit breakers or fuses. This protection prevents catastrophic damage from short circuits by quickly disconnecting the motor from the power supply in the event of a fault.
In addition to overload and short-circuit protection, motor starters are designed with safety features like emergency stop buttons and interlocks. These features ensure that the motor can be safely shut down in an emergency, preventing potential hazards and injuries.
Motor starters are essential in various industrial and commercial applications. They are used to control heavy-duty motors in conveyor belts, mixers, pumps, and compressors. By managing the initial surge of current and protecting the motor from overloads, motor starters ensure that operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Motor starters are also crucial in controlling the operation of elevators, cranes, and other lifting equipment. They help ensure that motors accelerate and decelerate smoothly, reducing mechanical stress and improving safety.
Motor starters control electric pumps used in water supply systems and irrigation. They provide a safe startup and protect the motor from damage during operation, ensuring reliable performance in critical applications.

When selecting a motor starter, factors such as the motor size, application type, and operational environment should be considered. The starter should match the motor’s voltage and current requirements while offering the necessary protection, such as overload and short-circuit protection.
For small motors, DOL starters may be sufficient, while larger motors may require more advanced starters like star-delta or soft starters to reduce inrush currents. VFDs are ideal for applications requiring precise speed control and energy efficiency.
Motor starters are essential for safe and efficient motor operation. They control startups, prevent overloads, and ensure smooth function. Understanding the different types and their applications helps you select the best solution for safety and reliability. Regular testing and maintenance are vital for optimal performance. By integrating intelligent motor control and protection, you can extend motor lifespan and enhance performance. Radin Electric offers advanced motor starter solutions to meet these needs effectively.
A: A motor starter is an electrical device used to safely start and stop motors. It prevents overloads and damage by controlling the current flow, ensuring efficient operation.
A: The main components of a motor starter are the contactor, overload relay, and motor control and protection switch. These components ensure the motor runs smoothly and safely.
A: A multi-function motor starter provides additional features like intelligent motor control and protection, offering advanced protection and more control over motor performance.
A: Overload protection is critical in preventing motor damage caused by excess current, extending the motor's lifespan, and ensuring safe operation.
A: Intelligent motor control and protection switches help optimize motor performance by automatically adjusting to load conditions, improving efficiency, and preventing failures.
A: While it's possible to use a motor starter without overload protection, it's highly discouraged, as it exposes the motor to risks of overheating and damage.